INTRODUCTION
L-Alpha glycerylphosphorylcholine (alpha-GPC or choline alfoscerate) is a choline-containing phospholipid. When ingested, alpha-GPC is metabolized into choline and glycerol-1-phosphate. Choline is a precursor of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, attention, and skeletal muscle contraction. Glycerol-1-phosphate is used to support cellular membranes.
Alpha-GPC appears to easily cross the blood-brain barrier and is rapidly absorbed. It is currently the best cholinergic for increasing plasma and brain choline levels.
Manufacture
Industrially, alpha-GPC is produced by the chemical or enzymatic deacylation of phosphatidylcholine enriched soya phospholipids followed by chromatographic purification. Alpha-GPC may also be derived in small amounts from highly purified soy lecithin as well as from purified sunflower lecithin.
| Synonyms | Choline glycerophosphate L-α-Phosphatidylcholine |
| CAS no. | 28319-77-9 |
| EINECS no. | 248-962-2 |
| Molecular formula | C8H20NO6P |
| Molecular weight | 257.22 |
| Structure | 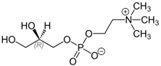 |
Applications
| Alpha-GPC is a prescription medication for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. It is available in two forms; one is taken by mouth, and the other is given as a shot. In the United States alpha-GPC is only available as a dietary supplement, mostly in products promoted to improve memory. |
| Alpha-GPC include treatment of various kinds of dementia, stroke, and “mini stroke” (transient ischemic attack, TIA). |
| Alpha GPC rapidly delivers choline to the brain across the blood–brain barrier and is a biosynthetic precursor of the acetylcholine neurotransmitter. |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | White to off white hygroscopic powder |
| Identification – TLC | – | Standard solution and test solution same spot, RF |
| Specific Optical Rotation | – | -2.4° ~ 2.8° |
| Water content | % | NMT 2.00 |
| pH | – | 4.5 to 7.0 |
| Assay | % | 98.50 – 100.00 |
| Chemical Tests | ||
| Sulfate | % | NMT 0.02 |
| Chloride | % | NMT 0.02 |
| Related substance | – | Spot not bigger than standard solution spot |
| Residual solvent | % | NMT 0.5 |
| Heavy metals | ppm | NMT 10.00 |
STORAGE
Store in an airtight and light resistant container, away from moisture.
PACKING
5 kg HDPE drum.
REGISTRATION / CERTIFICATION
ISO, FSSAI, HACCP, HALAL, KOSHER & GMP certified.
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
DL-Serine is a racemic mixture of both the D- and L-forms of the amino acid serine, which is a polar, nonessential amino acid. It is an α-amino acid characterized by its hydroxyl-containing side chain, which enables it to take part in numerous biochemical reactions and synthetic processes. It functions as a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids, including glycine and cysteine, underscoring its essential role in cellular metabolism. Moreover, it constitutes a critical pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents and drug candidates.
Ethyl vinyl ether is a reactive, flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor. Featuring two conjugated functional groups—an ether and an alkene—this molecule act as important building block, especially in polymer synthesis. Its applications span multiple industrial sectors, including semiconductors, coatings, inks, fragrances, adhesives, paints, oil viscosity modifiers and pharmaceuticals, with promising potential as a dietary supplement.
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is a common herb, also known as a hybrid mint. Its main components are oxygenated monoterpenes: alcohols, esters and ketones. Peppermint oleoresin microencapsulated powder is a white to off-white coloured powder produced from the seeds of the plant. In order to protect and maintain the stability of peppermint oil, microencapsulation is carried out through process optimization using the coacervation technique. This technique helps limit the loss and degradation of flavours and aromas during processing and storage. It offers versatile applications across multiple industries — from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and textiles.
5-Methyl-3-vinyl-2-oxazolidinone (V-MOX) is a highly reactive monomer valued for its low viscosity, mild odor, and excellent reactivity. It is widely used as a reactive diluent in UV-curable inks and coatings, where it enhances adhesion, produces brighter colors, and improves safety compared to conventional diluents. In addition, V-MOX serves as a key building block in the synthesis of kinetic hydrate inhibitor (KHI) polymers, which are applied in oil and gas production to prevent hydrate blockages in pipelines.
Zinc ricinoleate is the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a hydroxylated fatty acid derived mainly from castor oil (Ricinus communis). It appears as a white to slightly yellowish powder, waxy solid, or paste, depending on formulation. Its most valuable property is its ability to trap and absorb odor molecules such as amines, sulfides, and short-chain fatty acids, making it an essential ingredient in deodorant and odor-control products.
2-(tert-Butyl amino)ethyl methacrylate (TBAEMA) is a functional methacrylate monomer that contains a secondary amine group and a hydrophobic tert-butyl moiety, giving it excellent versatility in pH-responsive and adhesion-enhancing polymer systems.
It is valued in printing ink formulations for its ability to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and surface interaction.
