INTRODUCTION
Caffeine (anhydrous) is a naturally occurring methylxanthine derivative used as a CNS stimulant, to restore mental alertness and wakefulness in patients experiencing fatigue or drowsiness.
Manufacturing
Caffeine anhydrous is made from the seeds and leaves of green coffee plants. The word “anhydrous” means “without water.” After harvesting, caffeine is extracted from the plant matter and dehydrated. This produces a highly concentrated caffeine powder.
| Synonyms | Methyltheobromine 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine |
| CAS no. | 58-08-2 |
| EINECS no. | 200-362-1 |
| Molecular formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molecular weight | 194.19 |
| Structure | 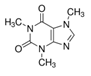 |
Applications
| Caffeine anhydrous is used as stimulant drug in |
|---|
| Food production |
| Beverage such as in coffee, tea, soda drink to stimulate the central nervous |
| Pharmaceutical |
| In Health and Personal care |
|---|
| Caffeine anhydrous is used as Fragrance Ingredient; Skin-Conditioning agent. |
| Primary short-term effects of Caffeine are: |
|---|
| Increasing resting heart rate |
| Psychostimulation |
| Constricting blood vessels |
| Dilating the bronchioles |
| Slightly increasing metabolic rate |
| Increasing urine production and gastric motility |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Description | – | A white crystalline powder; sublimes readily |
| Solubility | – | Sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in boiling water, slightly soluble in ethanol and in ether. It dissolves in concentrated solutions of alkali benzoates or salicylates. |
| Identification A | – | By IR absorption identical with Std. |
| Identification B | – | To Comply |
| Water | % | NMT 0.5 |
| Melting Range | °C | Between 235.0 – 237.5 after drying at 80°C for 4 hours |
| Residue on Ignition | % | NMT 0.1 |
| Arsenic | ppm | NMT 3.0 |
| Heavy Metals | % | NMT 0.001 |
| Readily Carbonizable Substances | – | The solution has no more color than matching Fluid D. |
| Residual solvents | – | To Comply |
| Other Alkaloids | – | No precipitate is formed |
| Chromatographic Purity – Any individual impurity | % | NMT 0.1 |
| Total impurity | % | NMT 0.1 |
| Assay | % | NLT 98.5 & NMT 101.0 on anhydrous basis |
STORAGE
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
PACKING
25 kg drum.
REGISTRATION / CERTIFICATION
ISO, FSSAI, HALAL, KOSHER, GMP & US-DMF.
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Iodine is anon-metallic, dark-grey/purple-black, lustrous, solid element. It is the heaviest and the rarest of stable halogens that can be found on the crust of earth.About fifty percent of all iodine produced and manufactured worldwide is used to form Organoiodine compounds. Iodine is an important element for many health-sustaining processes and essential for human thyroid health.
The product, acronymed Oct-NBE, is an organic compound with a cyclic ring system and a 8-membered hydrophobic chain. The structure renders the chemical special properties leading to its applications in diverse fields.
Nicotine is a hygroscopic, colorless to slight yellow, oily liquid, that is readily soluble in alcohol, ether or light petroleum. It is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic.
The product, acronymed ETD, is an organic compound with a fused bicyclic ring system and an ethylidene group. The structure renders the chemical special properties leading to its applications in diverse fields.
Sodium perchlorate monohydrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4•H2O. It is the common existence form of sodium perchlorate, which can gradually absorb water in the air to form the monohydrate. Sodium perchlorate monohydrate is white rhombic crystal which is highly soluble in water and in alcohol. Its capacity to undergo redox reactions, liberating oxygen atoms, has been harnessed in the preparation of specialty chemicals, including pharmaceutical intermediates and fine chemicals.
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound that is frequently abbreviated as PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in organic and organometallic compound synthesis because it is an effective reducing agent as well as a neutral ligand. At room temperature, PPh3 crystals are relatively air-stable and colourless.
Potassium chlorate holds significant importance across various industries due to its diverse applications. This white crystalline compound has been utilized for centuries as an essential ingredient in the production of matches, fireworks, and explosives, owing to its ability to release oxygen upon decomposition.
Podophyllotoxin is a non-alkaloid toxin lignan extracted from the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum species. It is an organic heterotetracyclic compound that has a Furonaphthodioxole skeleton bearing a 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl substituent.
Octadecylphosphonic acid (ODPA), a versatile chemical compound, serves as a surfactant and dispersant in applications spanning coatings, lubricants, and corrosion inhibition. With its hydrophobic octadecyl chain linked to a phosphonic acid group, it excels in surface modification, boosting adhesion in metal surfaces.
