INTRODUCTION
Ferrous Ascorbate is a combination of vitamin C and iron. Ferrum or iron helps to replenish the iron stores in the human body. Ascorbate contains vitamin C that improves iron levels in the body by increasing its absorption from different sources.
Manufacture
By reacting alkali or alkaline earth metals with ferrous sulfate, the corresponding ferrous salts are formed, which are then reacted with ascorbic acid in slightly acidic or neutral conditions in an aqueous medium. To obtain ferrous ascorbate, the mother liquor must be filtered.
| Synonyms | Ascorbic acid ferrous salt Vitamin C iron(II) salt L-(+)-Ascorbic acid iron(II) salt |
| CAS no. | 24808-52-4 |
| EINECS no. | 246-469-7 |
| Molecular formula | C12H16FeO12 |
| Molecular weight | 406.08 |
| Structure | 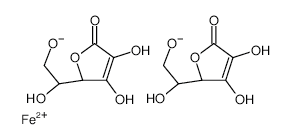 |
APPLICATIONS
Ferrous Ascorbate has several applications in the pharmaceutical industry and is a valuable component in many medications and supplements.
| Iron supplement | It is commonly used as an iron supplement in the pharmaceutical industry to treat iron-deficiency anemia. It is available in various forms such as tablets, capsules, and syrups. |
| Nutraceutical | It is also used as a nutraceutical, which is a dietary supplement that provides health benefits beyond basic nutrition. It is often used in combination with other vitamins and minerals to promote overall health and wellness. |
| Antioxidant | Ascorbate, the other component of Ferrous ascorbate, is a powerful antioxidant. Antioxidants help to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which can cause damage to cells and contribute to the development of various diseases. |
| Anti-inflammatory | Ascorbate also has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce inflammation in the body. This makes it useful in the treatment of conditions such as arthritis and other inflammatory disorders. |
| Immune system support | Ascorbate is also essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. It plays a vital role in the production of white blood cells and helps to protect the body against infections and diseases. |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | A dark violet colored powder |
| Solubility | – | Freely soluble in wáter |
| Identification A. Iron test B. Ascorbic test | – – | The solution will give blue colour A grey precipitate is formed |
| Loss on Drying | % | ≤ 10 |
| Heavy metals | ppm | ≤ 25 |
| pH (aq. solution) | % w/v | 1.0 |
| Assay (ODB) 1. Content of Iron 2. Content of Ascorbic acid | % % | 14.0 – 17.0 60.0 – 70.0 |
| Residual solvent | – | No organic solvent |
| Microbiological contamination 1. Total aerobic microbial count 2. Total Yeast & Mold count 3. Specific micro organisms a. Escherichia Coli b. Pseudonimas aeruginosa c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Salmonella. sp. | cfu/g cfu/g absent/g absent/g absent/g absent/10 g | ≤ 10(superscript)3 ≤ 10(superscript)2 Should comply Should comply Should comply Should comply |
PACKING
20 kg HDPE drum.
STORAGE
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
CERTIFICATION
GMP & DMF
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazonane (Me₃TACN) is a valuable macrocyclic tridentate ligand derived from 1,4,7-triazacyclononane. In Me₃TACN, each nitrogen atom is substituted with a methyl group, which significantly modifies its steric and electronic properties. Me₃TACN is widely used as a ligand in coordination chemistry due to its ability to form stable complexes with transition metals such as Cu, Ni, Fe, Mn, and Zn.
Adenosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside composed of adenine and ribose, present in all living cells. It plays a vital role in biochemical processes such as energy transfer (ATP/ADP), signal transduction, and regulation of physiological functions, and is widely used in pharmaceutical applications.
Methyl-2-Methoxy-5-Sulfamoyl Benzoate (MSMB) is a sulfur containing organic building block acting as a chemical intermediate. MSMB contains ester and sulfamoyl functional groups, which make it useful as a pharmaceutical and fine-chemical intermediate.
Imidazolidinyl urea is a widely used antimicrobial preservative in the cosmetic and personal care industry. It is a formaldehyde-releasing compound that effectively inhibits the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds, thereby extending the shelf life of formulations. Due to its broad-spectrum efficacy and cost-effectiveness, it is commonly used in rinse-off and leave-on products within regulated concentration limits.
Phosphorodiamidites are a unique class of phosphorus-based compounds characterized by one P–O bond and two P–N moieties. 2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite plays a crucial role in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Beyond their application as synthetic precursors for oligonucleotides, phosphorodiamidites have also been reported as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of industrially relevant polymers and flame-resistant materials, including adhesives, coatings, and laminates.
Ferric maltol is an oral iron complex composed of ferric iron (Fe³⁺) chelated with maltol, designed to improve iron absorption while reducing common gastrointestinal side effects associated with traditional iron salts. It is primarily used in the management of iron deficiency with better tolerability.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
