INTRODUCTION
Methylene blue (MB), a basic thiazine dye has been used clinically for about a century to treat numerous ailments. Primarily used in the treatment of methemoglobinemia, as an antidote in cyanide poisoning, as a biological stain, and as an oxidant-reduction indicator.
The intravenous form of MB is approved by the FDA for the treatment of pediatric and adult patients with acquired methemoglobinemia. MB is an investigational drug being developed by the University of Aberdeen and TauRx Therapeutics that has been shown in early clinical trials to be an inhibitor of Tau protein aggregation. The drug is also of potential interest for the treatment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
| Synonyms | Methylthioninium chloride Basic blue 9 (C.I. 52015) |
| CAS no. | 122965-43-9 (hydrate) 7220-79-3 (trihydrate) 61-73-4 (anhydrous) |
| EINECS no. | 602-909-3 (hydrate) 615-731-6 (trihydrate) 200-515-2 (anhydrous) |
| Molecular formula | C16H18N3S.Cl.xH2O |
| Molecular weight | 337.90 (hydrate & trihydrate) 319.85 (anhydrous) |
| Structure | 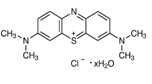 |
MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
| Methemoglobinemia | MB is employed as a medication for the treatment of methemoglobinemia |
| Combined with light | MB combined with light has been used to treat resistant plaque psoriasis |
| Urinary tract infection | MB is a component of a urinary analgesic/anti-infective/anti-spasmodic known as “Prosed DS”, a combination of phenyl salicylate, benzoic acid, hyoscyamine sulfate, and methenamine (aka hexamethylenetetramine and not to be confused with ‘methanamine’) |
| Cyanide poisoning | Since its reduction potential is similar to that of oxygen and can be reduced by components of the electron transport chain, large doses of methylene blue are sometimes used as an antidote to potassium cyanide poisoning |
| Dye or stain | MB is used in endoscopic polypectomy as an adjunct to saline or epinephrine and is used for injection into the submucosa around the polyp to be removed |
| Placebo | MB has been used as a placebo; physicians would tell their patients to expect their urine to change color and view this as a sign that their condition had improved |
| Ifosfamide toxicity | Another use of methylene blue is to treat Ifosfamide neurotoxicity |
| Shock | It has also been used in septic shock and anaphylaxis |
OTHER APPLICATIONS
| Redox indicator | MB is widely used as a redox indicator in analytical chemistry |
| Peroxide generator | MB is also a photosensitizer used to create singlet oxygen when exposed to both oxygen and light |
| Biological staining | In biology MB is used as a dye for number of different staining procedures, such as Wright’s stain and Jenner’s stain. Since it is a temporary staining technique, MB can also be used to examine RNA or DNA under the microscope or in a gel |
| Aquaculture | MB is used in aquaculture and by tropical fish hobbyists as a treatment for fungal infections |
Modes of action of Methylene Blue in SARS-CoV-2 infection complications (as per the current ongoing studies. Concrete data to be available soon)
| It inhibits SARS-CoV-2 spike ACE2 protein – protein interaction |
| To treat Cytokinin Storm which is one of the major reason for ADRs, Multiorgan Failure & Mortality |
| It relieves oxidative stress, ROS and free radicals |
| It increases systemic vascular resistance (SVR) in septic shock |
| It causes antifibrotic action in lungs |
SPECIFICATIONS
MB offered by Exsyn complies USP & EP pharmacopeia. Please ask our sourcing team if you need detailed specifications.
WRITTEN CONFIRMATION (WC)
ExSyn offers MB with WC certification, so it can be sold to the EU as an API for human consumption.
STORAGE
Temporary storage temperature is below 30°C
Long term storage temperature is 5°C ± 3°C
ExSyn offers MB on commercial scale and welcomes enquiries. No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please get in touch with us.
5-Methyl-3-vinyl-2-oxazolidinone (V-MOX) is a highly reactive monomer valued for its low viscosity, mild odor, and excellent reactivity. It is widely used as a reactive diluent in UV-curable inks and coatings, where it enhances adhesion, produces brighter colors, and improves safety compared to conventional diluents. In addition, V-MOX serves as a key building block in the synthesis of kinetic hydrate inhibitor (KHI) polymers, which are applied in oil and gas production to prevent hydrate blockages in pipelines.
Zinc ricinoleate is the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a hydroxylated fatty acid derived mainly from castor oil (Ricinus communis). It appears as a white to slightly yellowish powder, waxy solid, or paste, depending on formulation. Its most valuable property is its ability to trap and absorb odor molecules such as amines, sulfides, and short-chain fatty acids, making it an essential ingredient in deodorant and odor-control products.
2-(tert-Butyl amino)ethyl methacrylate (TBAEMA) is a functional methacrylate monomer that contains a secondary amine group and a hydrophobic tert-butyl moiety, giving it excellent versatility in pH-responsive and adhesion-enhancing polymer systems.
It is valued in printing ink formulations for its ability to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and surface interaction.
Commonly known as potassium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (KFSI), the compound has a three-carbon backbone bearing six fluorine atoms and two sulfonimide (-SO₂F) groups. The molecule’s architecture lends it both high chemical stability and useful reactivity. Because of its excellent ionic conductivity and thermal / electrochemical stability, it finds use in advanced electrolyte formulations—for example in lithium-ion and next-generation batteries, in ionic liquids, and in other electrochemical systems.
Colchicine is a naturally occurring alkaloid obtained primarily from the autumn crocus (Colchicum autumnale) and related species. It has been used in medicine for centuries, especially for the treatment of gout and Familial Mediterranean Fever. In modern medicine, Colchicine is valued also in conditions like pericarditis, Behçet’s disease, and certain dermatological and cardiac disorders.
1-Butylimidazole is a versatile organic heterocyclic compound belonging to the imidazole family, where a butyl group (–CH₂–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃) is attached to the nitrogen atom at the 1-position of the imidazole ring. Its applications span organic synthesis, materials science, and bioactive compound development due to its tunable physicochemical properties and structural versatility.
Atropine sulfate monohydrate is a chemical compound, specifically a salt of atropine and sulfuric acid, with one water molecule (monohydrate) attached. It is commonly used as a medication and in research due to its anticholinergic properties, meaning it blocks the effects of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors.
4-Aminobenzoic acid, commonly abbreviated as PABA, is an aromatic amine and carboxylic acid compound. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with an amino group (–NH₂) in the para position to a carboxylic acid group (–COOH).
2-Amino-5-Nitrophenol (5-NAP) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C₆H₆N₂O₃. It is a substituted phenol with both an amino group (-NH₂) and a nitro group (-NO₂) attached to a benzene ring, along with a hydroxyl group (-OH).
