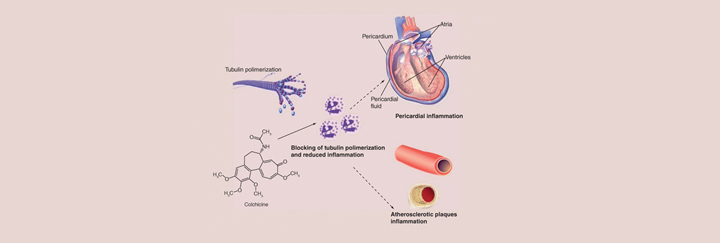
INTRODUCTION
Colchicine belongs to a class of drugs called Uricosuric agents.
It is an alkaloid used in the symptomatic relief of pain in attacks of gouty arthritis, pseudogout, sarcodial arthritis, calcific tendinitis and to treat the inflammatory symptoms of Familial Mediterranean Fever.
It appears as odourless or nearly odourless pale yellow needles or powder that darkens on exposure to light.
Manufacture
It is derived from the bulb-like corms of the Colchicum autumnale plant, also known as autumn crocus.
| Synonyms | N-[(7S)-1,2,3,10-Tetramethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl]-acetamide |
| CAS no. | 64-86-8 |
| EINECS no. | 200-598-5 |
| Molecular formula | C22H25NO6 |
| Molecular weight | 399.44 |
| Structure | 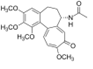 |
Applications
| Gout and Pseudogout | Colchicine has been known as a treatment for gout for several millenia. It is also recommended for the treatment of acute flares, as well as flare prophylaxis, in patients with pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis. |
| Familial Mediterranean Fever | Colchicine has been the treatment of choice for Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) a hereditary autoinflammatory condition since the 1970’s. |
| Uses in Dermatology | Colchicine has been reported to be an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment for numerous dermatologic diseases. Behçet’s disease, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, leukocytocastic vasculitis, Sweet’s syndrome and recurrent apthous stomatitis are some of the few dermatologic diseases in which treatment with colchicine has been studied. |
| New Potential Indications | The potential uses of colchicine have broadened significantly over the last few years as new studies have emerged demonstrating novel applications within oncology, immunology, cardiology, and dermatology. |
SPECIFICATIONS – EP/BP
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | Yellowish-White, amorphous or crystalline powder |
| Solubility | – | Very soluble in wáter, rapidly re-crystallizing from concentrated solutions as the sesquihydrate, freely soluble in Ethanol (96%), practically insoluble in Cyclohexane |
| Identification 1. By UV 2. By IR 3. By Chemical 4. By Chemical | – – – – | The ratio of absorbance measured at 243 nm to that measured 350 nm is 1.7 to 1.9 The IR absorption spectrum of the preparation of the test specimen and working standard, exhibits maxima only at the same wave lengths The organic layer is greenish-yellow A brownish-red colour develops |
| Appearance of solution | – | Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY3 (2.2.2, Method II) |
| Acidity or Alkalinity | – | Either the solution does not change colour or it become green. Not more tan 0.1 ml of 0.01 M Sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to blue |
| Specific optical rotation | – | -250° to -235°, calculated on the anhydrous substance |
| Related substances (by HPLC) 1. Impurity ‘A’ 2. Impurity ‘G’ 3. Impurity ‘E’ 4. Unspecified impurities 5. Total impurities | % % % % % | Max 3.0 Max 0.25 Max 0.20 Max 0.10 Max 4.0 |
| Impurity F | % | Max 0.2 |
| Ethyl acetate (by GC) | % | Max 6.0 |
| Water content (by KF) | % | Max 2.0% determined on 0.500 gm |
| Sulphated ash | – | Max 0.1% determined on 0.500 gm |
| Residual solvents (by HSGC) 1. Methanol 2. Acetone 3. Methylene Dichloride 4. Chloroform | ppm ppm ppm ppm | NMT 3000 NMT 5000 NMT 600 NMT 500 |
| Assay (Potentiometer) | % | 97.0 to 102.0 |
STORAGE
Store in a dry and well-ventilated area.
PACKING
1 kg aluminum foil in steel container.
REGISTRATION / CERTIFICATION
ISO, WHO-GMP, Written Confirmation (WC), DMF as per EP/BP/USP & Certificate of Suitability (CEP) to European monograph.
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Iodine is anon-metallic, dark-grey/purple-black, lustrous, solid element. It is the heaviest and the rarest of stable halogens that can be found on the crust of earth.About fifty percent of all iodine produced and manufactured worldwide is used to form Organoiodine compounds. Iodine is an important element for many health-sustaining processes and essential for human thyroid health.
The product, acronymed Oct-NBE, is an organic compound with a cyclic ring system and a 8-membered hydrophobic chain. The structure renders the chemical special properties leading to its applications in diverse fields.
Nicotine is a hygroscopic, colorless to slight yellow, oily liquid, that is readily soluble in alcohol, ether or light petroleum. It is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic.
The product, acronymed ETD, is an organic compound with a fused bicyclic ring system and an ethylidene group. The structure renders the chemical special properties leading to its applications in diverse fields.
Sodium perchlorate monohydrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4•H2O. It is the common existence form of sodium perchlorate, which can gradually absorb water in the air to form the monohydrate. Sodium perchlorate monohydrate is white rhombic crystal which is highly soluble in water and in alcohol. Its capacity to undergo redox reactions, liberating oxygen atoms, has been harnessed in the preparation of specialty chemicals, including pharmaceutical intermediates and fine chemicals.
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound that is frequently abbreviated as PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in organic and organometallic compound synthesis because it is an effective reducing agent as well as a neutral ligand. At room temperature, PPh3 crystals are relatively air-stable and colourless.
Potassium chlorate holds significant importance across various industries due to its diverse applications. This white crystalline compound has been utilized for centuries as an essential ingredient in the production of matches, fireworks, and explosives, owing to its ability to release oxygen upon decomposition.
Podophyllotoxin is a non-alkaloid toxin lignan extracted from the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum species. It is an organic heterotetracyclic compound that has a Furonaphthodioxole skeleton bearing a 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl substituent.
Octadecylphosphonic acid (ODPA), a versatile chemical compound, serves as a surfactant and dispersant in applications spanning coatings, lubricants, and corrosion inhibition. With its hydrophobic octadecyl chain linked to a phosphonic acid group, it excels in surface modification, boosting adhesion in metal surfaces.