INTRODUCTION
Acetonitrile (ACN) is a highly polar, volatile, colorless liquid with ethereal odor and is the simplest organic nitrile widely used as a solvent.
The nitrile group constitutes active part of the molecule. It participates in various reactions that lead to number of nitrogen containing organic molecules.
Manufacture
ACN is manufactured on large scale by addition of ammonia in propylene, acrylonitrile being the by-product.
| Synonyms | Methyl Cyanide Cyanomethane |
| CAS no. | 75-05-8 |
| EINECS no. | 200-835-2 |
| Molecular formula | C2H3N |
| Molecular weight | 41.05 |
| Structure | 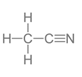 |
Industrial Applications
ACN has excellent solubilizing properties. These enable its use as a useful solvent in synthesis and purification processes of distillation and recrystallization.
Commonly occurring uses as solvent are in:
| High pressure liquid chromatographic (HPLC) analysis as an eluent. |
| Butadiene extraction in Petro refineries. |
| Manufacture of insulin, vitamins, amino acids and photographic films. |
| Lithium batteries. |
| Non-aqueous reactions that employ AlCl3 and PCl3. |
| Manufacture of flame retardants. |
| Extraction of fatty acids from vegetable oil. |
| Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes. |
| Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex catalysts. |
| Solvent for DNA synthesis and Peptide sequencing. |
| Solvent for spinning synthetic fibers. |
| Casting and moulding plastics. |
Intermediates
The nitrile group being reactive, ACN acts as a key raw material in production of:
| Acetamidine hydrochloride |
| Acetoguanamine |
| β-Aminocrotononitrile |
| 2,4-Dihydroxy acetophenone |
| 2,6-Dihydroxy acetophenone |
| Geranonitrile |
| Malononitrile |
| Triethyl orthoacetate |
| Sulphapyrimidines |
| O,N-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide |
Applications in APIs
As a key raw material in the early manufacturing stages of:
| Sulfisomidine | Antibacterial |
| Pyritinol | Nootropic |
| Cromolyn | Antiasthma / Antiallergic |
| Alprazolam | Anxiolytic |
| Diazoxide | Antihypertensive / Hyperglycemia |
| Triazolam | Hypnotic |
As an essential raw material in the ultimate synthesis step of:
| Amantadine | Antiviral / Antiparkinsonian |
| Sulphaphenazole | Antibacterial |
Agrochemicals
| Isoxaben | Herbicide |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | Clear colorless liquid, free from extraneous matter. |
| Identification (By GC) | – | Retention time of the main peak in the test sample chromatogram should match with that of the standard. |
| Purity (By GC) | % | Min 99.0 |
| Moisture Content (By KF) | % | Max 0.2 |
| Miscibility | – | Miscible with methanol. |
| Non-volatile matter | % | Max 0.1 |
REACH status
Acetonitrile offered by ExSyn is registered under EU REACH regulations.
STORAGE
Product is stored at ambient temperature.
PACKING
Drum & ISO-tank
ExSyn offers acetonitrile on commercial scale and welcomes enquiries. No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please get in touch with us.
5-Methyl-3-vinyl-2-oxazolidinone (V-MOX) is a highly reactive monomer valued for its low viscosity, mild odor, and excellent reactivity. It is widely used as a reactive diluent in UV-curable inks and coatings, where it enhances adhesion, produces brighter colors, and improves safety compared to conventional diluents. In addition, V-MOX serves as a key building block in the synthesis of kinetic hydrate inhibitor (KHI) polymers, which are applied in oil and gas production to prevent hydrate blockages in pipelines.
Zinc ricinoleate is the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a hydroxylated fatty acid derived mainly from castor oil (Ricinus communis). It appears as a white to slightly yellowish powder, waxy solid, or paste, depending on formulation. Its most valuable property is its ability to trap and absorb odor molecules such as amines, sulfides, and short-chain fatty acids, making it an essential ingredient in deodorant and odor-control products.
2-(tert-Butyl amino)ethyl methacrylate (TBAEMA) is a functional methacrylate monomer that contains a secondary amine group and a hydrophobic tert-butyl moiety, giving it excellent versatility in pH-responsive and adhesion-enhancing polymer systems.
It is valued in printing ink formulations for its ability to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and surface interaction.
Commonly known as potassium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (KFSI), the compound has a three-carbon backbone bearing six fluorine atoms and two sulfonimide (-SO₂F) groups. The molecule’s architecture lends it both high chemical stability and useful reactivity. Because of its excellent ionic conductivity and thermal / electrochemical stability, it finds use in advanced electrolyte formulations—for example in lithium-ion and next-generation batteries, in ionic liquids, and in other electrochemical systems.
Colchicine is a naturally occurring alkaloid obtained primarily from the autumn crocus (Colchicum autumnale) and related species. It has been used in medicine for centuries, especially for the treatment of gout and Familial Mediterranean Fever. In modern medicine, Colchicine is valued also in conditions like pericarditis, Behçet’s disease, and certain dermatological and cardiac disorders.
1-Butylimidazole is a versatile organic heterocyclic compound belonging to the imidazole family, where a butyl group (–CH₂–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃) is attached to the nitrogen atom at the 1-position of the imidazole ring. Its applications span organic synthesis, materials science, and bioactive compound development due to its tunable physicochemical properties and structural versatility.
Atropine sulfate monohydrate is a chemical compound, specifically a salt of atropine and sulfuric acid, with one water molecule (monohydrate) attached. It is commonly used as a medication and in research due to its anticholinergic properties, meaning it blocks the effects of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors.
4-Aminobenzoic acid, commonly abbreviated as PABA, is an aromatic amine and carboxylic acid compound. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with an amino group (–NH₂) in the para position to a carboxylic acid group (–COOH).
2-Amino-5-Nitrophenol (5-NAP) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C₆H₆N₂O₃. It is a substituted phenol with both an amino group (-NH₂) and a nitro group (-NO₂) attached to a benzene ring, along with a hydroxyl group (-OH).
