INTRODUCTION
Budesonide is in a class of medications called corticosteroids. It works by decreasing inflammation (swelling) in the digestive tract of people who have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. or in the kidney of people with nephropathy.
MANUFACTURE
It is manufactured by the reaction of 16α-hydroxyprednisolone (11β,16α,17α,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione) with butyraldehyde in dioxane, using perchloric acid as catalyst.
| Synonym | 16,17-Butylidenebis(oxy)-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione |
| CAS no. | 51333-22-3 |
| EINECS no. | 257-161-7 |
| Molecular formula | C25H34O6 |
| Molecular weight | 430.5 g/mol |
| Structure | 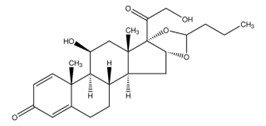 |
APPLICATIONS
| It is used for the treatment of: |
|---|
| Asthma |
| Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Allergic rhinitis |
| Eosinophilic esophagitis |
| Berger’s disease |
SPECIFICATIONS… (EP)
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | White or almost white, crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | – | Practically insoluble in water, Freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in alcohol (96%). |
| Identification | ||
| A) By IR Absorption | – | The IR spectrum of the sample should be concordant with that of a similar preparation of Budesonide standard. |
| B) By TLC | – | The principal spot of the test chromatogram should correspond to the principal spot of reference solution (a) at 254nm and 365nm. |
| C) By Chemical | – | The colour should fade and a clear solution remains. |
| D) By Chemical | – | The solution should turn blue. |
| Loss on drying | % | Not more than 0.5 |
| Epimer A (Second Peak) | % | 40.0 to 51.0 |
| Related Substances (By HPLC) | ||
| Impurity A | % | Not more than 0.2 |
| Impurity D | % | Not more than 0.2 |
| Impurity K | % | Not more than 0.2 |
| Impurity L | % | Not more than 0.2 |
| Unspecified impurities | % | Not more than 0.10 |
| Total impurities | % | Not more than 0.5 |
| Assay (By HPLC) (on dried substance) | % w/w | 97.5 to 102.0 |
| Residual Solvents | ||
| Methanol | ppm | Not more than 1000 |
| Dichloro Methane | ppm | Not more than 600 |
| n-butyraldehyde | ppm | Not more than 150 |
| Benzene | ppm | Not more than 2 |
| Dimethyl formamide | ppm | Not more than 880 |
PACKING
Fiber/HDPE drum.
STORAGE
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
CERTIFICATION
WHO–GMP, Written Confirmation for EU and CEP.
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Phosphorodiamidites are a unique class of phosphorus-based compounds characterized by one P–O bond and two P–N moieties. 2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite plays a crucial role in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Beyond their application as synthetic precursors for oligonucleotides, phosphorodiamidites have also been reported as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of industrially relevant polymers and flame-resistant materials, including adhesives, coatings, and laminates.
Ferric maltol is an oral iron complex composed of ferric iron (Fe³⁺) chelated with maltol, designed to improve iron absorption while reducing common gastrointestinal side effects associated with traditional iron salts. It is primarily used in the management of iron deficiency with better tolerability.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
DL-Serine is a racemic mixture of both the D- and L-forms of the amino acid serine, which is a polar, nonessential amino acid. It is an α-amino acid characterized by its hydroxyl-containing side chain, which enables it to take part in numerous biochemical reactions and synthetic processes. It functions as a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids, including glycine and cysteine, underscoring its essential role in cellular metabolism. Moreover, it constitutes a critical pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents and drug candidates.
Ethyl vinyl ether is a reactive, flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor. Featuring two conjugated functional groups—an ether and an alkene—this molecule act as important building block, especially in polymer synthesis. Its applications span multiple industrial sectors, including semiconductors, coatings, inks, fragrances, adhesives, paints, oil viscosity modifiers and pharmaceuticals, with promising potential as a dietary supplement.
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is a common herb, also known as a hybrid mint. Its main components are oxygenated monoterpenes: alcohols, esters and ketones. Peppermint oleoresin microencapsulated powder is a white to off-white coloured powder produced from the seeds of the plant. In order to protect and maintain the stability of peppermint oil, microencapsulation is carried out through process optimization using the coacervation technique. This technique helps limit the loss and degradation of flavours and aromas during processing and storage. It offers versatile applications across multiple industries — from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and textiles.
5-Methyl-3-vinyl-2-oxazolidinone (V-MOX) is a highly reactive monomer valued for its low viscosity, mild odor, and excellent reactivity. It is widely used as a reactive diluent in UV-curable inks and coatings, where it enhances adhesion, produces brighter colors, and improves safety compared to conventional diluents. In addition, V-MOX serves as a key building block in the synthesis of kinetic hydrate inhibitor (KHI) polymers, which are applied in oil and gas production to prevent hydrate blockages in pipelines.
