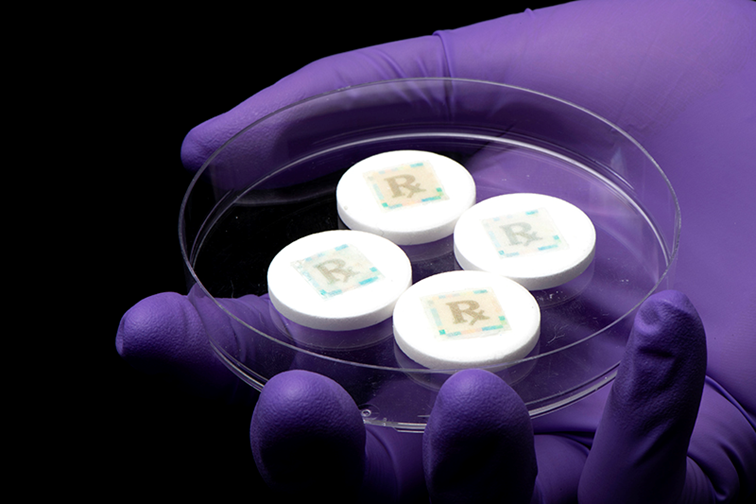
New anti-counterfeit technology, called a cyber-physical watermark, leverages edible fluorescent silk to identify medications.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has mandated that by 2023 medications have unit-level traceability through the Drug Supply Chain Security Act.
But how can this be achieved?
In a recent paper, researchers from Purdue University, US, revealed a technology that could meet this requirement.
Counterfeit medications and pharmaceutical products are just a click away from being purchased from online pharmacies via smartphone. However, the newly developed anti-counterfeiting technology could turn smartphones into lifesavers by allowing patients to simply take a picture of a cyber-physical watermark to confirm if a medication is real or not.
Purdue University biomedical engineers have developed new cyber-physical watermarks that allow people to check medication authenticity with a smartphone.
Young Kim, associate head for research and an associate professor in Purdue’s Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, says the continued rise of counterfeit medications, pharmaceutical products and medical supplies can be attributed to the increase of online pharmacies, many of which are unregulated.
To counteract the issue, the FDA is requiring medications have unit-level traceability by 2023. But, while pharmaceutical companies currently have the ability to track boxes or sheets of medications, the jump to adding traceability directly to pills could require adding numerous manufacturing and data management steps, according to Kim.
Kim’s team proposes using small cyber-physical watermarks to trace medications and confirm whether they are real or fake, as well as allowing patients to confirm dose and frequency, and access additional information on the medicine.
People can use a smartphone app to activate a new cyberphysical watermark to detect whether the medication they are taking is real or fake. Purdue biomedical engineers have developed the cyberphysical watermark as a way to reduce fake medications.

“A paper watermark is commonly used on currency and a passport to discourage counterfeiting, and we are affixing a watermark on an individual medicine that is readable by a smartphone camera to extract a hidden digital key,” Kim said. “Purdue has an excellent track record of watermarking and inkjet printing research. We are proud that we have extended such national security research into pharmaceuticals as counterfeit medicines are a national security problem.”
The cyber-physical watermark is printed on specialised edible fluorescent silk with FDA-approved food dye using an inkjet printer. According to the researchers, using fluorescent silk is not only beneficial because it makes it difficult for counterfeiters to duplicate the watermark, but also because engineers can change the biopolymer’s shape, structure and flexibility. The engineers also addressed how to use the technology with different smartphone models, photo quality and light.
“A person can take a photo under different light conditions and will have different images. It is the same issue when patients take photos of our watermark in their phone,” Kim explained. “The reference colours on the watermark’s periphery allow us to know the true colour value of the watermarked image as each smartphone has different spectral sensitivity.”
Placed on pills using a simple sugar glue, the smallest size of watermark the team could produce is 5mm by 5mm. While the team has had success with solid pills, it is working also on developing technology for liquids.
Cyber-physical watermark technology could be used first on name-brand medications and restricted narcotics before being rolled out on over-the-counter medications and generics.
The economic impact of biosimilars on the Australian health care system is now clearer, with data revealing their role in reducing market expenditure and driving price competition.
The Chinese Golden Week impacts Ocean Freight Shippers for two main reasons:
Donald Trump’s tariffs of 50% have come into force on most US imports from India. India’s giant generic pharmaceuticals sector and its electronics and petroleum products are exempt from the tariffs. Aluminium, steel and copper remain at 25%, but job-heavy sectors such as textiles, jewellery, seafood and leather are squarely in the line of fire.
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has published the updated proposal to restrict per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) under the EU’s chemicals regulation, REACH. The update has been prepared by the authorities from Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway and Sweden, who submitted the initial proposal in January 2023.
Most chemicals exported from the 27 member countries of the European Union into the US will be subject to a 15% tariff on top of their selling prices under an agreement signed on July 27 between the US and the European Commission.
We’re thrilled to announce a new strategic alliance between ExSyn, Exim-Indis and simABs, a leading EU-based biologics manufacturer known for its patented continuous flow technology in antibody production.
The global trade landscape is undergoing significant changes following the announcement of new reciprocal tariffs by the United States government. Recent developments indicate significant shifts in global trade dynamics, with key policy adjustments, ongoing negotiations, and evolving logistics patterns. Below is a summary of the latest developments.
In January 2025, the US FDA published a draft regulatory guidance entitled “The Considerations for Use of Artificial Intelligence to Support Regulatory Decision-Making for Drug and Biological Products”.
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLMs) is rapidly reshaping clinical research and drug development.