INTRODUCTION
3-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) is a peroxycarboxylic acid. A white solid, it is used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. MCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling.
Manufacture
MCPBA can be prepared by reacting m-Chlorobenzoyl chloride with a basic solution of hydrogen peroxide, followed by acidification.
| Synonyms | 3-Chlorobenzenecarboperoxoic acid |
| CAS no. | 937-14-4 |
| EINECS no. | 213-322-3 |
| Molecular formula | C7H5ClO3 |
| Molecular weight | 172.57 |
| Structure | 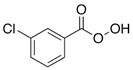 |
Applications
MCPBA is versatile applicable as peracid for use in laboratories.
| Main areas are the oxidation of: |
|---|
| aldehydes and ketones to esters (Bayer-Villiger-Oxidation) |
| olefines to epoxides |
| sulfides to sulfoxides and sulfones |
| amines to nitroalkanes, nitroxides or N-oxides |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | White to off white moist crystalline powder with lumps |
| Color | – | Colorless |
| Clarity | – | Clear to slightly hazy |
| 3-Chloro per benzoic acid (by Iodometry) | % | Min 70.0 |
| 3-Chloro benzoic acid | % | Max 12.0 |
| m-Chlorobenzoyl peroxide (by HPLC) | % | Max 0.2 |
| Water (by KF) | % | Balance |
STORAGE
Due to relatively unstable nature of organic peroxide a loss of quality can be detected over a period. To minimize the loss of quality, recommended maximum storage temperature (Ts max.) for each peroxide. Ts max.: 2 – 8°C)
PACKING
20 kg UN approved drum.
REACH status
MCPBA offered by ExSyn is registered under EU REACH regulations.
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Imidazolidinyl urea is a widely used antimicrobial preservative in the cosmetic and personal care industry. It is a formaldehyde-releasing compound that effectively inhibits the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds, thereby extending the shelf life of formulations. Due to its broad-spectrum efficacy and cost-effectiveness, it is commonly used in rinse-off and leave-on products within regulated concentration limits.
Phosphorodiamidites are a unique class of phosphorus-based compounds characterized by one P–O bond and two P–N moieties. 2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite plays a crucial role in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Beyond their application as synthetic precursors for oligonucleotides, phosphorodiamidites have also been reported as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of industrially relevant polymers and flame-resistant materials, including adhesives, coatings, and laminates.
Ferric maltol is an oral iron complex composed of ferric iron (Fe³⁺) chelated with maltol, designed to improve iron absorption while reducing common gastrointestinal side effects associated with traditional iron salts. It is primarily used in the management of iron deficiency with better tolerability.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
DL-Serine is a racemic mixture of both the D- and L-forms of the amino acid serine, which is a polar, nonessential amino acid. It is an α-amino acid characterized by its hydroxyl-containing side chain, which enables it to take part in numerous biochemical reactions and synthetic processes. It functions as a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids, including glycine and cysteine, underscoring its essential role in cellular metabolism. Moreover, it constitutes a critical pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents and drug candidates.
Ethyl vinyl ether is a reactive, flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor. Featuring two conjugated functional groups—an ether and an alkene—this molecule act as important building block, especially in polymer synthesis. Its applications span multiple industrial sectors, including semiconductors, coatings, inks, fragrances, adhesives, paints, oil viscosity modifiers and pharmaceuticals, with promising potential as a dietary supplement.
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is a common herb, also known as a hybrid mint. Its main components are oxygenated monoterpenes: alcohols, esters and ketones. Peppermint oleoresin microencapsulated powder is a white to off-white coloured powder produced from the seeds of the plant. In order to protect and maintain the stability of peppermint oil, microencapsulation is carried out through process optimization using the coacervation technique. This technique helps limit the loss and degradation of flavours and aromas during processing and storage. It offers versatile applications across multiple industries — from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and textiles.