According to the World Health Organization, about 785 million people around the world lack a clean source of drinking water. Despite the vast amount of water on Earth, most of it is seawater and freshwater accounts for only about 2.5% of the total. One of the ways to provide clean drinking water is to desalinate seawater. The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) has announced the development of a stable performance electrospun nanofiber membrane to turn seawater into drinking water by membrane distillation process.:
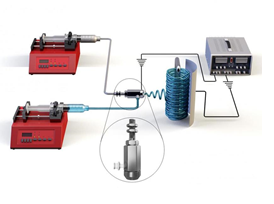
Membrane wetting is the most challenging issue in membrane distillation. If a membrane exhibits wetting during membrane distillation operation, the membrane must be replaced. Progressive membrane wetting has been especially observed for long-term operations.
If a membrane gets fully wetted, the membrane leads to inefficient membrane distillation performance, as the feed flow through the membrane leading to low-quality permeate.
A research team in KICT, led by Dr. Yunchul Woo, has developed co-axial electrospun nanofiber membranes fabricated by an alternative nano-technology, which is electrospinning. This new desalination technology shows it has the potential to help solve the world’s freshwater shortage. The developed technology can prevent wetting issues and also improve the long-term stability in membrane distillation process. A three-dimensional hierarchical structure should be formed by the nanofibers in the membranes for higher surface roughness and hence better hydrophobicity.
The co-axial electrospinning technique is one of the most favorable and simple options to fabricate membranes with three-dimensional hierarchical structures. Dr. Woo’s research team used poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) as the core and silica aerogel mixed with a low concentration of the polymer as the sheath to produce a co-axial composite membrane and obtain a superhydrophobic membrane surface. In fact, silica aerogel exhibited a much lower thermal conductivity compared with that of conventional polymers, which led to increased water vapor flux during the membrane distillation process due to a reduction of conductive heat losses.
Most of the studies using electrospun nanofiber membranes in membrane distillation applications operated for less than 50 hours although they exhibited a high-water vapor flux performance. On the contrary, Dr. Woo’s research team applied the membrane distillation process using the fabricated co-axial electrospun nanofiber membrane for 30 days, which is 1 month.
The co-axial electrospun nanofiber membrane performed a 99.99% salt rejection for 1 month. Based on the results, the membrane operated well without wetting and fouling issues, due to its low sliding angle and thermal conductivity properties.
The co-axial electrospun nanofiber membrane performed a 99.99% salt rejection for 1 month. Based on the results, the membrane operated well without wetting and fouling issues, due to its low sliding angle and thermal conductivity properties.
Temperature polarization is one of the significant drawbacks in membrane distillation. It can decrease water vapor flux performance during membrane distillation operation due to conductive heat losses. The membrane is suitable for long-term membrane distillation applications as it possesses several important characteristics such as, low sliding angle, low thermal conductivity, avoiding temperature polarization, and reduced wetting and fouling problems whilst maintaining super-saturated high water vapor flux performance.
Dr. Woo’s research team noted that it is more important to have a stable process than a high-water vapor flux performance in a commercially available membrane distillation process. Dr. Woo said that “the co-axial electrospun nanofiber membrane have strong potential for the treatment of seawater solutions without suffering from wetting issues and may be the appropriate membrane for pilot-scale and real-scale membrane distillation applications.”
Reference:
https://www.chemeurope.com/en/news/1171742/making-seawater-drinkable-in-minutes.html
The floating traffic jams off ports. The multiplying costs of moving freight. The resulting shortages of goods. All of this had seemed like an unpleasant memory confined to the COVID-19 pandemic. But no such luck!
An ocean container capacity crunch has hit global trade just as peak shipping season starts, with freight spot rates up some 30% over the past few weeks and heading higher.
The first joint Europe-wide assessment of the drivers and impact of chemical pollution by the European Environment Agency (EEA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has concluded that, despite progress in some areas, “more work is still needed to reduce the impact of harmful substances on human health and the environment”. Key findings include:
The severe drought which has forced the Panama Canal, one of the world’s busiest trade passages, to limit daily crossings could impact global supply chains during a period of high demand.
In the early hours of March 26, the Singapore-flagged ship Dali, loaded with 5,000 containers, slammed into Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge, causing the 1.6-mile (2.5-kilometer) bridge to collapse in a matter of seconds. The Dali was departing for Colombo when the disaster struck. Initial fears were confirmed that half a dozen people lost their lives in the accident.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries constantly seek innovative methods to enhance product stability, solubility, bioavailability and ease of use. Within this realm, CDMOs [Contract Development & Manufacturing Organizations] serve as invaluable partners in the development and production of high-quality drug products.
Chinese New Year 2024 is upon us, disrupting logistics from Asia starting Feb 10th. This event is expected to impact global shipping until Feb 21. Freight rates from Asia has skyrocketed with rates to the US surging by 3.5X and Europe by 6X.
Amid ongoing Red Sea diversions by shipping giants like Maersk, CMA, logistics managers are globally confronting a dual challenge of escalating ocean and air freight prices alongside cargo disruptions due to
Why will CM be the next generation on quality?
