INTRODUCTION
N2-Isobutyryl-2′-O-methyl-guanosine (IBG) is a modified nucleoside that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential therapeutic and industrial applications. IBG is a derivative of guanosine, a nucleoside that is a building block of RNA and DNA.
Manufacture
By alkylation of O6-trimethylsilylethyl-3′,5′-di-tert-butylsilanediyl guanosine.
| Synonym | N-[9-[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-3-methoxyoxolan-2-yl]-6-oxo-1H-purin-2-yl]-2-methylpropanamide |
| CAS no. | 63264-29-9 |
| Molecular formula | C15H21N5O6 |
| Molecular weight | 367.36 g/mol |
| Structure | 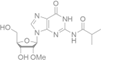 |
APPLICATIONS
| N2-isobutyryl-2′-OMe-guanosine (IBG) has potential applications as follows: |
|---|
| It’s a modified nucleoside that can be used as an activator for DNA synthesis. |
| A useful intermediate in the synthesis and probes of novel nucleic acids. |
| Detecting DNA/RNA changes is the popular use of this fluorescent chemical. |
| Medical Research : IBG has been studied for its role in drug development, with promising results in preclinical studies. |
| Clinical Trials : IBG has also been studied in clinical trials for its potential therapeutic effects in various diseases, including viral infections and cancer. |
| Environmental research – It has been studied for its effects on ecosystems and its potential role in pollution management. |
| Industrial research – IBG has been used in manufacturing processes to improve product quality and efficiency, with health and safety considerations being a major concern. |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | White to off-white powder |
| 1HNMR | – | To conform the structure |
| MS | – | To conform the structure |
| Purity by HPLC | % | ≥ 98.0 |
| Assay (by QNMR) | % | ≥ 97% |
| Solvent content by GC | % | ≤ 3.0 |
| Water content | % | ≤ 3.0 |
PACKING
25 kg HDPE drum with inner liner
STORAGE
Recommended storage between 2°C to 8°C
No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please contact us.
Methyl-2-Methoxy-5-Sulfamoyl Benzoate (MSMB) is a sulfur containing organic building block acting as a chemical intermediate. MSMB contains ester and sulfamoyl functional groups, which make it useful as a pharmaceutical and fine-chemical intermediate.
Imidazolidinyl urea is a widely used antimicrobial preservative in the cosmetic and personal care industry. It is a formaldehyde-releasing compound that effectively inhibits the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds, thereby extending the shelf life of formulations. Due to its broad-spectrum efficacy and cost-effectiveness, it is commonly used in rinse-off and leave-on products within regulated concentration limits.
Phosphorodiamidites are a unique class of phosphorus-based compounds characterized by one P–O bond and two P–N moieties. 2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite plays a crucial role in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Beyond their application as synthetic precursors for oligonucleotides, phosphorodiamidites have also been reported as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of industrially relevant polymers and flame-resistant materials, including adhesives, coatings, and laminates.
Ferric maltol is an oral iron complex composed of ferric iron (Fe³⁺) chelated with maltol, designed to improve iron absorption while reducing common gastrointestinal side effects associated with traditional iron salts. It is primarily used in the management of iron deficiency with better tolerability.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
DL-Serine is a racemic mixture of both the D- and L-forms of the amino acid serine, which is a polar, nonessential amino acid. It is an α-amino acid characterized by its hydroxyl-containing side chain, which enables it to take part in numerous biochemical reactions and synthetic processes. It functions as a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids, including glycine and cysteine, underscoring its essential role in cellular metabolism. Moreover, it constitutes a critical pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents and drug candidates.
Ethyl vinyl ether is a reactive, flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor. Featuring two conjugated functional groups—an ether and an alkene—this molecule act as important building block, especially in polymer synthesis. Its applications span multiple industrial sectors, including semiconductors, coatings, inks, fragrances, adhesives, paints, oil viscosity modifiers and pharmaceuticals, with promising potential as a dietary supplement.