INTRODUCTION
The aromatic is a liquid with a pleasant odor. The active methoxy group attached to a benzene ring renders a high amount of reactivity to the molecule. Worldwide, anisole is commercially produced by methylation of phenol.
| Synonyms | Methoxybenzene Phenyl Methyl Ether Methyl Phenyl Ether |
| CAS no. | 100-66-3 |
| EINECS no. | 202-876-1 |
| Molecular formula | C7H8O |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| Structure | 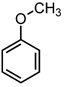 |
APPLICATIONS
Anisole is used in various industry verticals including but not limited to manufacture of API, colorants, cosmetics, flavor & fragrance chemicals, polymerization inhibitors, antioxidants, and agrochemicals. It is also consumed as solvent in various chemicals processes.
| Pharmaceuticals | The sweet aromatic is a key starting compound in the manufacture of Tamoxifen, Guaifenesin, Carvedilol, Ranolazine and Methocarbamol. In the process, anisole is first converted into Guaiacol, which is an antioxidant. Guaiacol is then used to synthesize some of the above APIs. |
| Agrochemicals | The methoxylated benzene acts as an insect pheromone and it also finds usage in manufacture of Ancymidole (a plant growth regulator) and Methoxychlor (an insecticide). |
| Flavors, Fragrances, and Cosmetics | The aromatic compound is extensively employed, thanks to its odor, for production of F&F chemicals such as Anethole, p-anisaldehyde, Guaiacol, 4-methoxyacetophenone, etc. From the last compound, cosmetic ingredient Avobenzone is manufactured. |
| Inhibitor | A feeble but important use of anisole is in production of methyl ether of hydroquinone (MEHQ), which is one of the universal polymerization inhibitors. |
| Colorant | Anisole is a KRM in the manufacture of the dye Disperse Blue 73 from Acid Blue 45. |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | Clear colorless liquid |
| Purity by GC | % | NLT 99.5 |
| Phenol Content by GC | ppm | NMT 50 |
| KF Moisture | % | NMT 0.1 |
| Iron | ppm | NMT 5 |
REACH status
Anisole offered by ExSyn is registered as Transported Isolated Intermediate (TII) under the EU REACH regulation.
STORAGE
Product is stored at ambient temperature.
PACKING
The product is offered in drum packing as well as ISO-tanks.
ExSyn offers this compound on commercial scale and welcomes enquiries. No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice ! If you need any additional information or SDS, please get in touch with us.
Blown Castor Oil (15-17 Poise) is a modified grade of Castor oil. The “15-17 Poise” specification refers to its viscosity range, indicating a medium-viscosity blown oil suitable for industrial applications requiring improved body, tackiness, and elasticity compared to regular castor oil.
Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) is a is a tertiary amine that is ethanolamine having two N-methyl substituents. It is clear & colourless to pale yellow liquid with ammoniacal odor. DMAE is stable at room temperature and is completely miscible with water as well as organic solvents such as alcohols and ethers. It decomposes at high temperatures. It is a versatile chemical intermediate primarily used as a curing agent for polyurethane foams and epoxy resins.
1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazonane (Me₃TACN) is a valuable macrocyclic tridentate ligand derived from 1,4,7-triazacyclononane. In Me₃TACN, each nitrogen atom is substituted with a methyl group, which significantly modifies its steric and electronic properties. Me₃TACN is widely used as a ligand in coordination chemistry due to its ability to form stable complexes with transition metals such as Cu, Ni, Fe, Mn, and Zn.
Adenosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside composed of adenine and ribose, present in all living cells. It plays a vital role in biochemical processes such as energy transfer (ATP/ADP), signal transduction, and regulation of physiological functions, and is widely used in pharmaceutical applications.
Methyl-2-Methoxy-5-Sulfamoyl Benzoate (MSMB) is a sulfur containing organic building block acting as a chemical intermediate. MSMB contains ester and sulfamoyl functional groups, which make it useful as a pharmaceutical and fine-chemical intermediate.
Imidazolidinyl urea is a widely used antimicrobial preservative in the cosmetic and personal care industry. It is a formaldehyde-releasing compound that effectively inhibits the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds, thereby extending the shelf life of formulations. Due to its broad-spectrum efficacy and cost-effectiveness, it is commonly used in rinse-off and leave-on products within regulated concentration limits.
Phosphorodiamidites are a unique class of phosphorus-based compounds characterized by one P–O bond and two P–N moieties. 2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite plays a crucial role in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Beyond their application as synthetic precursors for oligonucleotides, phosphorodiamidites have also been reported as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of industrially relevant polymers and flame-resistant materials, including adhesives, coatings, and laminates.
Ferric maltol is an oral iron complex composed of ferric iron (Fe³⁺) chelated with maltol, designed to improve iron absorption while reducing common gastrointestinal side effects associated with traditional iron salts. It is primarily used in the management of iron deficiency with better tolerability.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is one of the most important phospholipids derived from soya lecithin and represents a key structural component of cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine 90% refers to a highly purified grade where the PC content is enriched to around 90% through specialized extraction and purification steps.
