INTRODUCTION
Phenyl chloroformate (PCF), an organic, volatile liquid, is an important reactant in chemical syntheses. It forms a series of intermediates that are further consumed to produce APIs, agrochemicals, and polymers. The chloroformate is also employed in proteomic research and itself is a phosgenation reagent.
Manufacture
Phenyl chloroformate is manufactured by phosgenation of phenol. Less hazardous synthesis route involves phenol, MDC, and triphosgene.
| Synonyms | Chloroformic acid phenyl ester Phenyl chloridocarbonate |
| CAS no. | 1885-14-9 |
| EINECS no. | 217-547-8 |
| Molecular formula | C7H5ClO2 |
| Molecular weight | 156.6 |
| Structure | 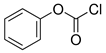 |
Applications in APIs
Chloroformic acid phenyl ester is a key intermediate in the production of APIs:
| API | Therapeutic Category |
|---|---|
| Rilmenidine | Anti-hypertensive |
| Sorafenib | Kinase inhibitor |
| Droxicam | Anti-inflammatory |
| Camazepam | Depressant |
| Leuprorelin | Prostate cancer treatment |
| Xamoterol hemifumerate | Cardiac stimulant |
Applications in Intermediate Syntheses
PCF forms an important raw material for the following intermediate compounds:
| 1,4-Beneznedimethanol |
| Ethyl phenyl carbonate |
| Piperidine-2-ethanol |
| Cbz-D-phenylalaninol |
| 4,6-dimethoxy-2(phenoxycarbonyl)aminopyrimidine |
| Phenyl carbamate |
| Benzyl phenyl carbonate |
Applications in Agrochemicals
PCF is used to manufacture sulphonyl urea herbicides such as Amidosulfuron and Flazasulfuron.
Other Applications
The chloroformate exhibits further versatility as:
| Precursor of phenyl mixed anhydrides which are couplers in peptide synthesis |
| Dehydrating agent to convert amides into nitriles |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test | Unit | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | – | Colorless to yellow liquid |
| Purity | % | Min 99.0 |
| Organic solvent | % | Max 1.0 |
| Phenol | % | Max 0.1 |
| Diphenyl carbonate | % | Max 1.0 |
| Hydrolysable chlorine | ppm | Max 3000 |
| Moisture | % | Max 0.3 |
STORAGE
The product is stored at ambient temperature.
PACKING
– 225 kg UN-approved MS Composite drum
– ISO-tank
REACH Status
Not registered yet.
ExSyn offers PCF on commercial scales and welcomes enquiries. No matter the quantity you need, our exceptional quality and service will make ExSyn your supplier of choice! If you need any additional information or SDS, please get in touch with us.
Indorez® Kota Resin is a modified non self-cured phenolic resin, it can increase rubber adhesion to steel, polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and other fabric cord. It’s an adhesive agent, acts as methylene acceptor, can 100% replace resorcinol and resorcinol resins in resorcinol- formaldehyde-silica, enhance adhesion between rubber and reinforcing materials.
Glyceryl Stearate Citrate (GSC) is a plant-derived, biodegradable emulsifier commonly used in cosmetics and personal-care products. It functions primarily as an anionic oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier, helping blend oils and water into smooth, stable creams and lotions. Its natural origin and gentle profile make it popular in eco-certified, organic, and sensitive-skin formulations.
DL-Serine is a racemic mixture of both the D- and L-forms of the amino acid serine, which is a polar, nonessential amino acid. It is an α-amino acid characterized by its hydroxyl-containing side chain, which enables it to take part in numerous biochemical reactions and synthetic processes. It functions as a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids, including glycine and cysteine, underscoring its essential role in cellular metabolism. Moreover, it constitutes a critical pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents and drug candidates.
Ethyl vinyl ether is a reactive, flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor. Featuring two conjugated functional groups—an ether and an alkene—this molecule act as important building block, especially in polymer synthesis. Its applications span multiple industrial sectors, including semiconductors, coatings, inks, fragrances, adhesives, paints, oil viscosity modifiers and pharmaceuticals, with promising potential as a dietary supplement.
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is a common herb, also known as a hybrid mint. Its main components are oxygenated monoterpenes: alcohols, esters and ketones. Peppermint oleoresin microencapsulated powder is a white to off-white coloured powder produced from the seeds of the plant. In order to protect and maintain the stability of peppermint oil, microencapsulation is carried out through process optimization using the coacervation technique. This technique helps limit the loss and degradation of flavours and aromas during processing and storage. It offers versatile applications across multiple industries — from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and textiles.
5-Methyl-3-vinyl-2-oxazolidinone (V-MOX) is a highly reactive monomer valued for its low viscosity, mild odor, and excellent reactivity. It is widely used as a reactive diluent in UV-curable inks and coatings, where it enhances adhesion, produces brighter colors, and improves safety compared to conventional diluents. In addition, V-MOX serves as a key building block in the synthesis of kinetic hydrate inhibitor (KHI) polymers, which are applied in oil and gas production to prevent hydrate blockages in pipelines.
Zinc ricinoleate is the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a hydroxylated fatty acid derived mainly from castor oil (Ricinus communis). It appears as a white to slightly yellowish powder, waxy solid, or paste, depending on formulation. Its most valuable property is its ability to trap and absorb odor molecules such as amines, sulfides, and short-chain fatty acids, making it an essential ingredient in deodorant and odor-control products.
2-(tert-Butyl amino)ethyl methacrylate (TBAEMA) is a functional methacrylate monomer that contains a secondary amine group and a hydrophobic tert-butyl moiety, giving it excellent versatility in pH-responsive and adhesion-enhancing polymer systems.
It is valued in printing ink formulations for its ability to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and surface interaction.
Commonly known as potassium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (KFSI), the compound has a three-carbon backbone bearing six fluorine atoms and two sulfonimide (-SO₂F) groups. The molecule’s architecture lends it both high chemical stability and useful reactivity. Because of its excellent ionic conductivity and thermal / electrochemical stability, it finds use in advanced electrolyte formulations—for example in lithium-ion and next-generation batteries, in ionic liquids, and in other electrochemical systems.